An operator is a symbol that tells the compiler to perform certain mathematical or logical operation.
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Increment and Decrement Operators
- Conditional Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Special Operators
- Extraction Operator ( >> )
- Insertion Operator ( << )
- Scope resolution operator ( :: )
- Arithmetic Operators
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Assignment Operators
- Increment and Decrement Operators
- Conditional Operators
- Bitwise Operators
- Special Operators
- Extraction Operator ( >> )
- Insertion Operator ( << )
- Scope resolution operator ( :: )
-> Arithmetic Operators :
Arithmetic operators are used for mathematical calculation. C++ supports following arithmetic operation.
- + : Addition or unary plus
- - : Subtraction or unary minus
- * : Multiplication
- / : Division
- % : Modulo division
-> Relational Operators :
Relational operators are used to compare two numbers and taking decisions based on their relation. Relational expressions are used in decision statements such as if, for, while, etc...
- < : Less than
- <= : Less than or equal to
- > : Greater than
- >= : Greater than or equal to== : Is equal to
- != : Is not equal to
-> Logical Operators :
Logical operators are used to test more than one condition and make decisions.
- && : Logical AND ( Both non zero then true,either is zero then false)
- | | : Logical OR ( Both zero then false,,either is non zero then true)
- ! : Logical NOT (non zero then false,zero then true)
-> Assignment Operators :
Assignment operators are used to assign the result of an expression to a variable. C++ also supports shorthand assignment operators which simplify operation with assignment.
- = : Assign value of right side to left side
- += : a+=1 is same as a=a+1
- -= : a-=1 is same as a=a-1
- *= : a*=1 is same as a=a*1
- /= : a/=1 is same as a=a/1
- %= : a%=1 is same as a=a%1
-> Increment and Decrement Operators :
These are special operators in c++ which are generally not found in other languages.
- ++ : Increments value by 1.
a++ is postfix, the expression is evaluated first and then the value is incremented.
Ex. a=10;b=a++; after this statement, a=11,b=10.
++a is prefix, the value is incremented first and then the expression is evaluated.
Ex. a=10;b=++a; after this statement, a=11,b=11.
- -- : Decrements value by 1.
a-- is postfix, the expression is evaluated first and then the value is incremented.
Ex. a=10;b=a--; after this statement, a=9,b=10.
--a is prefix, the value is decremented first and then the expression is evaluated.
Ex. a=10;b=++a; after this statement, a=10,b=9.
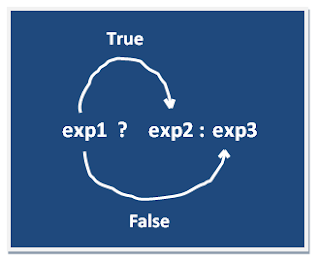
-> Conditional Operators :
A ternary operator is known as Conditional Operator.exp1? exp2: exp3 if exp1 is true then execute exp2 otherwise exp3
Ex: x= (a>b) ?a:b; which is same as
if(a>b)
x=a;
else
x=b;
-> Bitwise Operators :
Bitwise operator are used to perform operation bit by bit. Bitwise operators may not be applied to float or double.
- & : Bitwise AND
- | : Bitwise OR
- ^ : Bitwise exclusive OR
- << : shift left (shift left means multiply by 2)
- >> : shift left (shift right means multiply by 2)
-> Special Operators :
- & : Address operator, it is used to determine address of the variable.
- * : Pointer operator, it is used to declare pointer variable and to get value from it.
- , : Comma operator, it is used to link the related expression together.
- sizeof : It returns the number of bytes the operand occupies.
- . : Member selection operator, used in structure.
- -> : Member selection operator, used in pointer to structure.
-> Extraction operator( >> ) :
Extraction operator( >> ) is used with cin to input data from keyboard.
-> Insertion operator( << ) :
Insertion operator( << ) is used with cout to output data from keyboard.
-> Scope resolution operator( :: ) :
Scope resolution operator( :: ) is used to define the already declared member functions of the class.